
Discrete probability distribution is a type of probability distribution that shows all possible values of a discrete random variable along with the associated probabilities. In other words, a discrete probability distribution gives the likelihood of occurrence of each possible value of a discrete random variable.
Geometric distributions, binomial distributions, and Bernoulli distributions are some commonly used discrete probability distributions. This article sheds light on the definition of a discrete probability distribution, its formulas, types, and various associated examples.
| 1. | What is Discrete Probability Distribution? |
| 2. | Discrete Probability Distribution Formula |
| 3. | Discrete Probability Distribution Types |
| 4. | How To Find Discrete Probability Distribution? |
| 5. | FAQs on Discrete Probability Distribution |
A discrete probability distribution and a continuous probability distribution are two types of probability distributions that define discrete and continuous random variables respectively. A probability distribution can be defined as a function that describes all possible values of a random variable as well as the associated probabilities.
A discrete probability distribution can be defined as a probability distribution giving the probability that a discrete random variable will have a specified value. Such a distribution will represent data that has a finite countable number of outcomes. There are two conditions that a discrete probability distribution must satisfy. These are given as follows:
Suppose a fair dice is rolled and the discrete probability distribution has to be created. The possible outcomes are . Thus, the total number of outcomes will be 6. All numbers have a fair chance of turning up. This means that the probability of getting any one number is 1 / 6. Using this data the discrete probability distribution table for a dice roll can be given as follows:
| x | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P(X = x) | 1 / 6 | 1 / 6 | 1 / 6 | 1 / 6 | 1 / 6 | 1 / 6 |
A discrete random variable is used to model a discrete probability distribution. There are two main functions associated with such a random variable. These are the probability mass function (pmf) and the probability distribution function or cumulative distribution function (CDF).
The probability mass function can be defined as a function that gives the probability of a discrete random variable, X, being exactly equal to some value, x. This function is required when creating a discrete probability distribution. The formula is given as follows:
The cumulative distribution function gives the probability that a discrete random variable will be lesser than or equal to a particular value. The value of the CDF can be calculated by using the discrete probability distribution. Its formula is given as follows:
The mean of a discrete probability distribution gives the weighted average of all possible values of the discrete random variable. It is also known as the expected value. The formula for the mean of a discrete random variable is given as follows:
The discrete probability distribution variance gives the dispersion of the distribution about the mean. It can be defined as the average of the squared differences of the distribution from the mean, \(\mu\). The formula is given below:
Var[X] = ∑(x - \(\mu\)) 2 P(X = x)
A discrete probability distribution is used in a Monte Carlo simulation to find the probabilities of different outcomes. The most commonly used types of discrete probability distributions are given below.
A Bernoulli distribution is a type of a discrete probability distribution where the random variable can either be equal to 0 (failure) or be equal to 1 (success). The probability of getting a success is p and that of a failure is 1 - p. It is denoted as X ∼ Bernoulli (p). The pmf is expressed as follows:
P(X = x) = \(\left\ p &,if \: x = 1 \\ 1-p & , if \: x = 0 \end\right.\)
A binomial distribution is a discrete probability distribution that gives the success probability in n Bernoulli trials. The probability of getting a success is given by p. It is represented as X ∼ Binomial(n, p). The pmf is given as follows:
A geometric distribution is another type of discrete probability distribution that represents the probability of getting a number of successive failures till the first success is obtained. It is given by X ∼ G(p). The formula for the pmf is given as follows:
P(X = x) = (1 - p) x p, where p is the success probability of the trial.
Poisson distribution is a discrete probability distribution that is widely used in the field of finance. It gives the probability that a given number of events will take place within a fixed time period. The notation is written as X ∼ Pois(\(\lambda\)), where \(\lambda>0\). The pmf is given by the following formula:
A discrete probability distribution can be represented either in the form of a table or with the help of a graph. To find a discrete probability distribution the probability mass function is required. In other words, to construct a discrete probability distribution, all the values of the discrete random variable and the probabilities associated with them are required. Suppose a fair coin is tossed twice. Say, the discrete probability distribution has to be determined for the number of heads that are observed. The steps are as follows:
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| P(X = x) | 1 / 4 = 0.25 | 2 / 4 = 0.5 | 1 / 4 = 0.25 |
A histogram can be used to represent the discrete probability distribution for this example.

Related Articles:
Important Notes on Discrete Probability Distribution
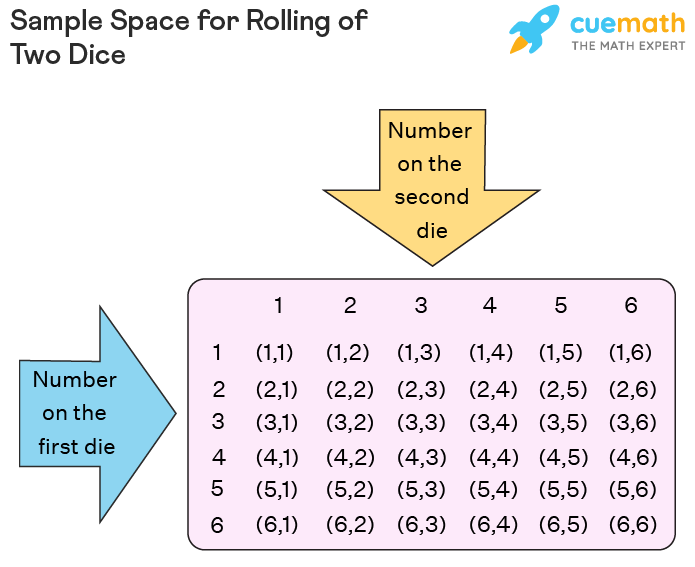
Example 1: Suppose a pair of fair dice are rolled. Let X be the random variable representing the sum of the dice. Construct a discrete probability distribution for the same. Solution: The sample space for rolling 2 dice is given as follows: Thus, the total number of outcomes is 36. The possible values of X range between 2 to 12. X = 2 means that the sum of the dice is 2. This can happen only when (1, 1) is obtained. Hence, P(X = 2) = 1 / 36. Using a similar process, the discrete probability distribution can be represented as follows:
| x | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P(X = x) | 1 / 36 | 2 / 36 | 3 / 36 | 4 / 36 | 5 / 36 | 6 / 36 | 5 / 36 | 4 / 36 | 3 / 36 | 2 / 36 | 1 / 36 |

The graph of the discrete probability distribution is given as follows
Example 2: Given a discrete probability distribution, find the value of k.| x | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P(X = x) | 0.2 | 0.5 | k | 0.1 |
Solution: For a discrete probability distribution, ∑P(X = x) =1.
By using this we get,
0.2 + 0.5 + k + 0.1 = 1
k + 0.8 = 1
k = 1 - 0.8 = 0.2
Answer: k = 0.2
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P(X = x) | 0.44 | 0.36 | 0.15 | 0.04 | 0.01 |
Solution: The formula for the expected value of a discrete probability distribution is E[X] = ∑x P(X = x)
E[X] = (0)(0.44) +(1)(0.36) + (2)(0.15) + (3)(0.04) + (4)(0.01)
= 0.82
Answer: E[X] = 0.82

Math will no longer be a tough subject, especially when you understand the concepts through visualizations.
A discrete probability distribution is used to model the probability of each outcome of a discrete random variable. This distribution is used when the random variable can only take on finite countable values.
The two key requirements for a discrete probability distribution to be valid are:
The steps to construct a discrete probability distribution are as follows:
The mean of a random variable, X, following a discrete probability distribution can be determined by using the formula E[X] = ∑x P(X = x).
To find the variable of a random variable following a discrete probability distribution apply the formula Var[X] = ∑(x - \(\mu\)) 2 P(X = x). Here, \(\mu\) is the mean of the distribution.
The expected value of a random variable following a discrete probability distribution can be negative. For example, the expected inflation rate can either be negative or positive.
A normal distribution can have an infinite set of values within a given interval. Thus, a normal distribution is not a discrete probability distribution. It falls under the category of a continuous probability distribution.